Asteroid 2024 YR4 will now virtually definitely miss Earth in 2032
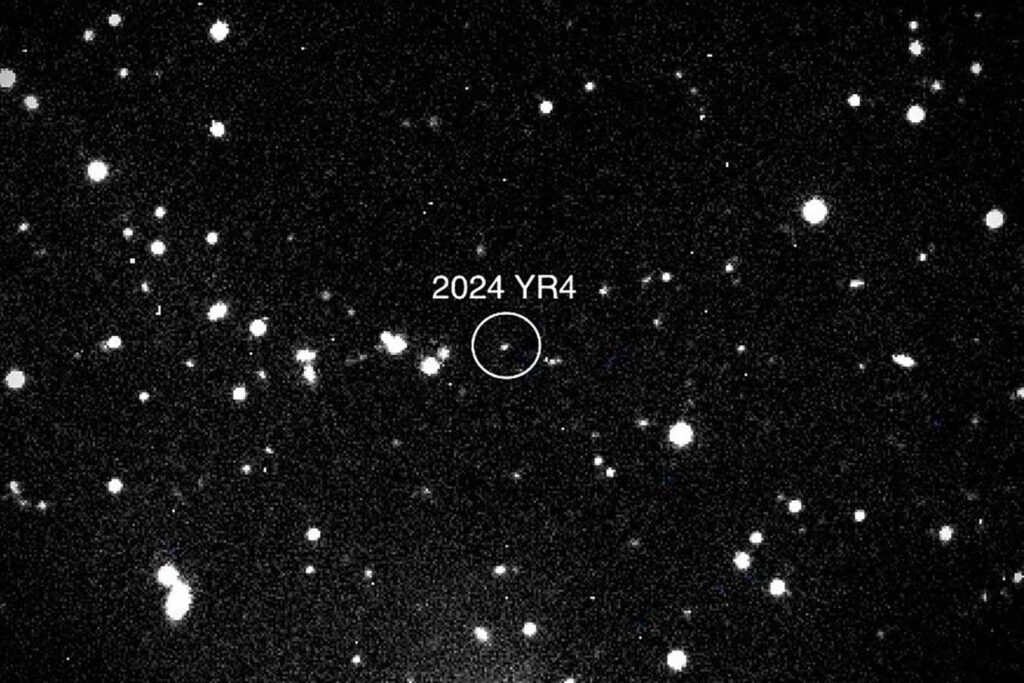


Astronomers have raced to look at asteroid 2024 YR4
NASA/Magdalena Ridge 2.4m telescope/New Mexico Institute of Expertise/Ryan
The world’s house businesses have diminished the probabilities of asteroid 2024 YR4 impacting Earth to under 1 per cent, which strongly suggests {that a} probably devastating collision might be averted. Nevertheless, the asteroid will nonetheless most likely go terribly close to to our planet, giving astronomers a uncommon alternative to look at an asteroid up shut.
“We aren’t anticipating the impression likelihood to rise again above 1 per cent for the shut method with Earth in 2032,” says Richard Moissl on the European Area Company (ESA). “The more than likely additional growth is an extra drop within the impression likelihood, seemingly even to 0.”
Alarms about asteroid 2024 YR4 have been first raised in December final 12 months, when astronomers discovered it is perhaps on a collision course for Earth in 2032. It seems to be between 40 and 90 metres huge and will generate a lethal blast ought to it hit a metropolis. Within the following weeks, the world’s telescopes and house businesses intently tracked its trajectory, honing its future path with larger precision. It reached its highest impression danger on 17 February, with a 1-in-32 probability, however within the days after, this fell to 1-in-67, or a 1.5 per cent danger.
On 20 February, new observations led to a pointy downgrade of this danger, with NASA placing it at a 0.27 per cent probability of impression, or 1-in-360, and ESA even decrease, at 0.16 per cent, or 1-in-625. These scores put it at a 1 on the 10-point Torino scale used to evaluate the hazard posed by such objects. That rating is down from 3, which means 2024 YR4 is now thought-about certainly one of many low-risk asteroids which can be found annually, however that in the end miss Earth.
That is excellent news, says Gareth Collins at Imperial Faculty London, however the asteroid will nonetheless be helpful as a dry run for our planetary defence techniques and for scientific functions. “That is nonetheless one thing that may make a spectacularly shut method. If the danger of hitting was as excessive because it was, it should be coming very near us,” he says.
NASA, ESA and house corporations that have been sketching out doable schemes to deflect the asteroid will most likely proceed planning, says Niklas Voigt at OHB, a German house firm. Voigt and his crew had begun occupied with a mission to divert 2024 YR4, and the brand new danger doesn’t change that, he says. “The danger decreased, however in the meanwhile we’re nonetheless continuing with work on the subject.”
The shut method might nonetheless be a superb alternative to check our skill to deflect asteroids, says Voigt – the one earlier try to do that was NASA’s DART mission, which efficiently modified the trajectory of the 160-metre-wide asteroid Dimorphos in 2022. Or we might construct a satellite tv for pc to ship to 2024 YR4, he says, just like ESA’s Ramses satellite tv for pc – as a result of journey to look at the asteroid Apophis, which is ready to go near Earth in 2029.
A last choice on what to do about 2024 YR4 most likely gained’t be made till deliberate observations in March utilizing the James Webb Area Telescope. In addition to gathering trajectory information, this may higher assess the scale and composition of the asteroid. That info might be then fed to the United Nations-backed Area Mission Planning Advisory Group, which can determine on a greatest plan of action across the finish of April. “These are extremely helpful workout routines for locating out the pinch factors to make choices, in an effort to nonetheless have time to do one thing wise upfront,” says Collins. “Completely, these committees will nonetheless be assembly, however they’ll most likely be much less nerve-racking.”
Whereas the probabilities of an Earth impression have plummeted, the danger of 2024 YR4 hitting the moon have risen to 1.2 per cent, up from 0.3 per cent. There’s a “distinct chance of that quantity rising additional,” says Moissl. “The precise results for an impression on the moon from an object of this measurement are nonetheless underneath analysis.”
The response to this object has additionally been a helpful rehearsal for different asteroids of concern that crop up, says Collins. “We wish to keep away from, in future, a cry wolf scenario the place the general public will get so used to this risk that they assume, ‘oh, it by no means occurs’.”
Matters: