Vulnerability Will increase for Crab, Squid, and Different Marine Species in California Waters


Rising water temperatures, acidification, and deoxygenation are disrupting marine ecosystems worldwide. These modifications threaten culturally and economically vital species, in the end endangering the livelihoods that rely upon them. To handle marine species battling local weather change, it’s important to establish probably the most weak ecosystems and species.
A research carried out by the College of California, Santa Cruz, goals to assist Californian fisheries adapt by creating climate-ready administration methods. The analysis staff collaborated with the California Division of Fish and Wildlife (CDFW), fisheries scientists from the Nationwide Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), and specialists from the Nature Conservancy and the California Ocean Safety Council to evaluate the local weather vulnerability of 34 key aquatic species.
“The outcomes are hanging,” stated Timothy Frawley, an assistant mission scientist at UC Santa Cruz’s Institute of Marine Sciences and lead creator of the research, in a press launch. “A few of California’s most economically and culturally essential fisheries are among the many most weak to projected environmental modifications.”
Local weather Change Impression on Marine Species
Key components influencing species vulnerability embody reproductive fee, habitat vary, and susceptibility to ocean acidification. Oceanographic modifications — akin to rising sea floor temperatures, altered salinity, declining subsurface oxygen ranges, and sea-level rise — additionally play a essential position.
One of many first noticeable shifts is in species distribution. As marine organisms adapt to altering environments, some — akin to Pacific herring and market squid — are shifting northward. This shift may push them past the attain of native fisheries, creating financial challenges. Conversely, species just like the Pacific bonito could discover Californian waters extra appropriate, presenting new fishing alternatives.
Learn Extra: Poop of the Ocean’s Tiniest Organisms Might Fight Local weather Change
Classifying Vulnerability
The researchers used Local weather Vulnerability Assessments (CVA) to gauge species’ susceptibility to environmental change. The system ranks species on a scale from blue (least weak) to crimson (most weak).
Findings counsel that between 2030 and 2060, 12 p.c of the 34 species studied will fall into the high-risk orange and crimson classes. This proportion is projected to rise to 53 p.c between 2070 and 2100. The research notes that these outcomes align with ongoing climate-driven modifications already noticed in marine ecosystems.
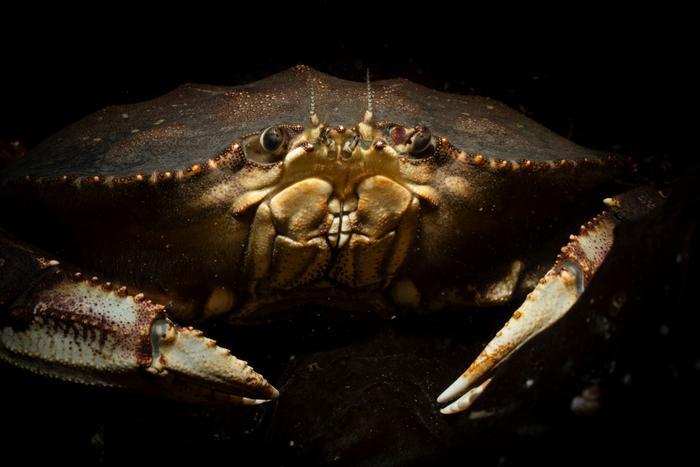
Species with restricted mobility, akin to crimson abalone — a sea snail—are notably weak as a result of they can not simply relocate in response to environmental modifications and thus labeled as extremely in danger. Different species, together with Pacific herring, Dungeness crab, Pismo clam, market squid, California spiny lobster, and pink shrimp, might also attain essential vulnerability ranges if local weather impacts intensify.
These species play a significant position in California’s economic system. Dungeness crab alone contributes roughly $45 million yearly to native and regional economies. Fisheries recognized as extremely weak have already skilled vital declines, additional underscoring the necessity for proactive administration methods.
How Fisheries Face the Future
Frawley emphasizes that the fishing business depends upon an enormous community of employees to perform effectively. Past boat crews, the business depends on dock employees, processing plant employees, and consumers. Scientists play a vital position in establishing sustainable harvest ranges and guaranteeing long-term viability.
“My expertise as a fisherman has impressed me to focus my work as a marine scientist on supporting coastal communities by offering them with the data wanted to raised navigate danger and uncertainty,” Frawley acknowledged within the launch.
Native assessments are essential, as species that migrate to completely different areas could keep away from extinction however nonetheless create challenges for regional fisheries. When fish populations shift past fishermen’s attain, their livelihoods undergo. Understanding these developments upfront permits fisheries to adapt whereas prioritizing conservation efforts.
The research means that extra versatile administration approaches will likely be mandatory to deal with climate-driven fluctuations in species distribution and inhabitants dynamics. Adjusting fishing rules to mirror these modifications will likely be key to sustaining each marine biodiversity and the fishing business within the years to come back.
Learn Extra: Carbon Is Robbing Crabs of Their Senses
Article Sources
Our writers at Discovermagazine.com use peer-reviewed research and high-quality sources for our articles, and our editors overview for scientific accuracy and editorial requirements. Evaluate the sources used under for this text:
Having labored as a biomedical analysis assistant in labs throughout three nations, Jenny excels at translating complicated scientific ideas – starting from medical breakthroughs and pharmacological discoveries to the most recent in diet – into participating, accessible content material. Her pursuits prolong to matters akin to human evolution, psychology, and quirky animal tales. When she’s not immersed in a preferred science e-book, you’ll discover her catching waves or cruising round Vancouver Island on her longboard.