Scientists Say They Discovered a New Colour People Have By no means Seen Earlier than : ScienceAlert

For the primary time, people may need glimpsed a rainbow of coloration that lies simply past our sight – together with a “blue-green of unprecedented saturation”.
You have by no means seen it earlier than as a result of you possibly can’t. It exists in a colorspace that our eyes don’t have any entry to.
Not less than, not naturally. Researchers on the College of California, Berkeley and the College of Washington now declare to have discovered a technique to hijack the retina and artificially increase the pure human coloration gamut.
Like Dorothy in The Wizard of Oz, the workforce thinks they’ll open our eyes to an entire new world of hues.
Their proof lies in an ‘Oz’ prototype – which might alter the best way that coloration alerts are handed from eye cell to eye cell and on to the mind. These activation patterns are not possible to attain beneath pure viewing situations, clarify the researchers.
The prototype works by flashing a laser gentle with a single monochromatic coloration (normally noticed as inexperienced) at particular person color-capturing cone cells.
Usually, each coloration we see stimulates a number of cone cells in our retina (of which there are greater than six million).
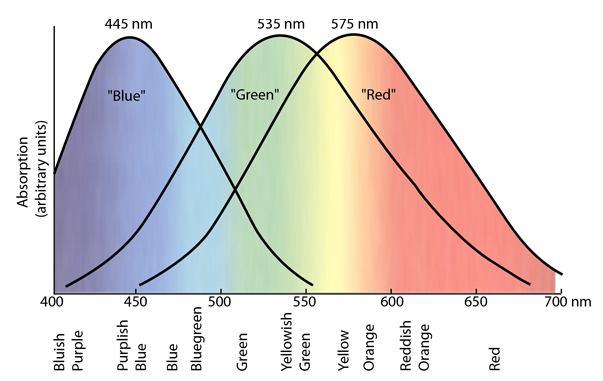
People are normally trichromats, that means we have now three various kinds of cone cells – delicate to lengthy, medium, and quick (L, M, S) wavelengths of sunshine within the seen spectrum.
L cones specialise in purple, M in inexperienced, and S in blue. When their alerts converge and mix on their technique to the mind, they kind the colour spectrum we all know and love.
As you possibly can see under, the M cone (inexperienced) sensitivity perform overlaps utterly with purple and blue cones. This implies there isn’t a wavelength of sunshine that stimulates solely the M cones beneath pure situations.
The Oz prototype will get round that by immediately capturing a laser at solely the M cones. Theoretically, this might create a coloration message for the mind that it’s unfamiliar with.
In experiments to check that concept, three individuals mounted their gaze on a impartial grey background whereas a inexperienced laser gentle flashed at their retinas. As anticipated, the colour sign from only a small group of focused M cells was not perceived as any identified coloration by the mind.
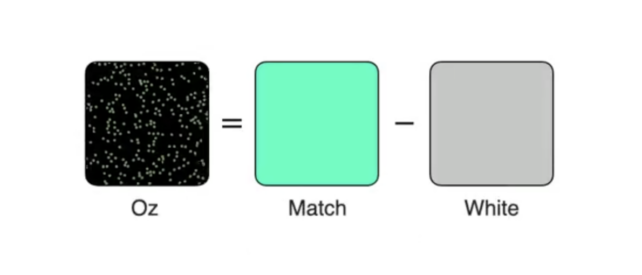
Contributors could not match the colour they have been seeing when given purple, inexperienced, and blue gentle to combine. That they had so as to add heaps of white gentle to desaturate it sufficient.
The workforce of researchers, led by electrical engineer James Fong from Berkeley, named the brand new coloration that individuals noticed “olo”, and its closest seen counterpart seems within the “match” field within the picture under.
Then, Fong and his colleagues had individuals view a shifting dot whereas focusing on just some cone cells with the Oz microdoses.
By doing so, they declare individuals perceived “completely different colours of the rainbow, unprecedented colours past the pure human gamut, and imagery like sensible purple traces or rotating dots on an olo background.”
In different phrases, the brand new rainbow of colours, in the event that they do exist, might theoretically be seen in movies in addition to photos.
Whereas Fong and colleagues argue their work supplies “unequivocal proof” of a brand new coloration, College of London imaginative and prescient scientist John Barbur, who was not concerned within the examine, instructed BBC’s Hafsa Kalil that this declare is “open to argument”.
Barbur considers the power to focus on a small variety of cones a “technological feat”, however he additionally factors out that this might affect the perceived brightness of a hue, presumably intensifying a identified coloration versus producing an entire new one.
As all the time with prototypes, there are limitations. The colours perceived by individuals utilizing the Oz technique have been on the sting of their imaginative and prescient, simply off their mounted level of focus. That is as a result of peripheral cone cells are much less densely packed right here and simpler to focus on. These cells, nevertheless, are inclined to have decrease acuity, that means they do not produce as away from an image.
The workforce hopes to proceed their work on the Oz prototype within the hope it could possibly probe the visible system at a cell degree, and possibly even deal with these with coloration blindness.
“Oz represents a brand new class of experimental platform for imaginative and prescient science and neuroscience, which strives for full management of the primary neural layer to the mind, programmability of each photoreceptor’s activation at each cut-off date,” write Fong and colleagues.
“Our prototype is an advance towards this class of neural management, and we reveal its skill to precisely ship microdoses to focus on cones.”
The examine was revealed in Science Advances.