How small are the elemental particles of the Universe? | by Ethan Siegel | Begins With A Bang! | Feb, 2025
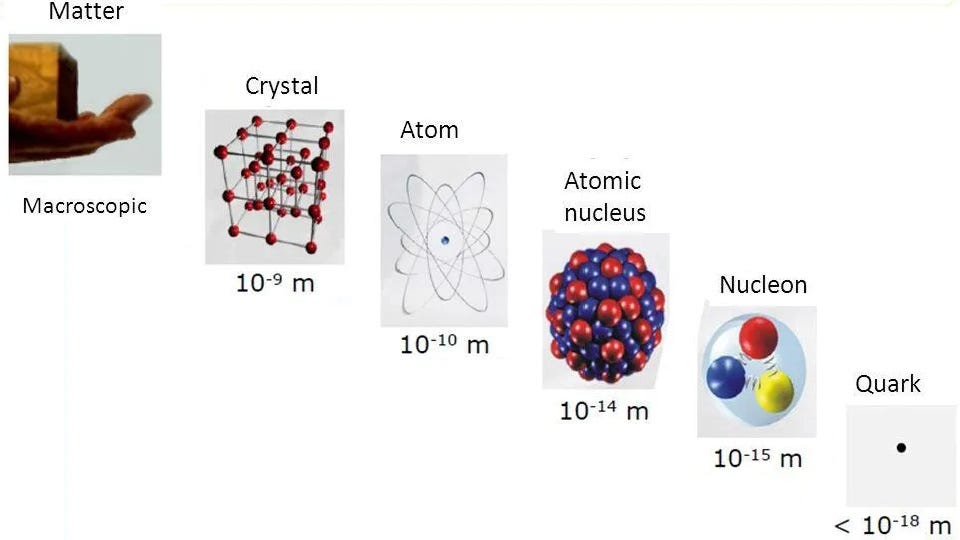
Once we divide matter into its elementary, indivisible elements, are these particles really point-like, or is there a finite minimal dimension?
Think about that you just needed to know what the matter round you was made from, at a elementary stage. How would you go about determining the reply? You would possibly assume to strategy the issue by taking a chunk of that matter and splitting it into small chunks, after which taking a kind of chunks and additional splitting it into tinier items, and so forth and so forth, till you would break up it now not. If you reached your restrict, and located a part that was now not splitable into something smaller, that might function the most effective approximation of “elementary” you would arrive at. When you uncover a part of matter that’s now not divisible into smaller elements, that’s an inexpensive strategy to outline elementary.
For a lot of the nineteenth century, we thought that atoms have been the elemental constituents of matter; the Greek phrase that our work atom derives from, ἄτομος, actually means “uncuttable.” At this time, we all know that atoms themselves aren’t really indivisible, however may be break up into nuclei and electrons, and that whereas we can not break up the electron, nuclei may be damaged up into protons and neutrons, which might…