Supersonic planes are inching towards takeoff. That could possibly be an issue.
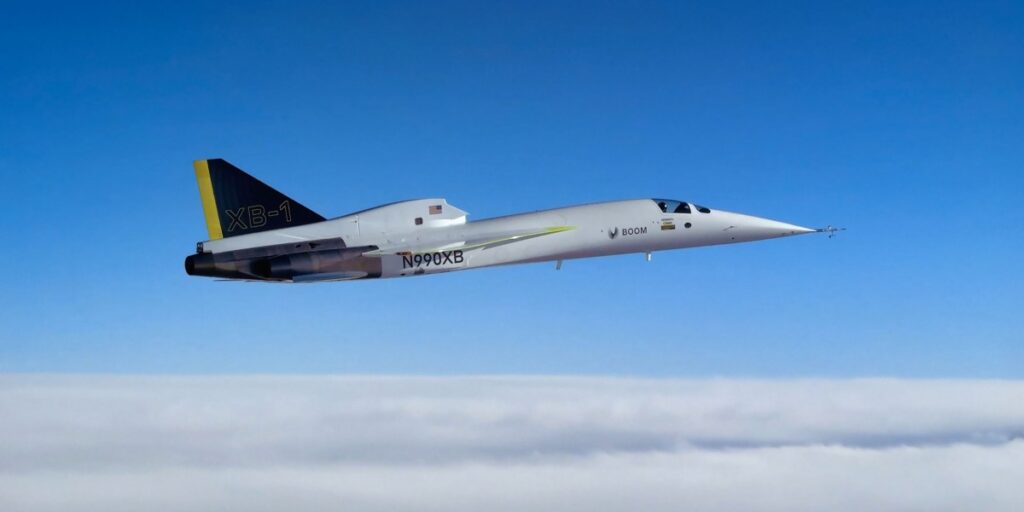

Growth plans to begin business operation with a scaled-up model of the XB-1, a 65-passenger jet referred to as Overture, earlier than the tip of the last decade, and it has already offered dozens of planes to clients together with United Airways and American Airways. However as the corporate inches towards that purpose, specialists warn that such efforts will include a hefty local weather price ticket.
Supersonic planes will burn considerably extra gas than present plane, leading to larger emissions of carbon dioxide, which fuels local weather change. Supersonic jets additionally fly larger than present business planes do, introducing atmospheric results that will heat the planet additional.
In response to questions from MIT Know-how Evaluate, Growth pointed to different fuels as an answer, however these stay in restricted provide—and so they may have restricted use in reducing emissions in supersonic plane. Aviation is a big and rising contributor to human-caused local weather change, and supersonic applied sciences may develop the sector’s air pollution, slightly than make progress towards shrinking it.
XB-1 follows a protracted historical past of world supersonic flight. People first broke the sound barrier in 1947, when Chuck Yeager hit 700 miles per hour in a analysis plane (the pace of sound at that flight’s altitude is 660 miles per hour). Simply over twenty years later, in 1969, the primary supersonic business airliner, the Concorde, took its first flight. That plane often traveled at supersonic speeds till the final one was decommissioned in 2003.
Amongst different points (just like the nuisance of sonic booms), one of many main downfalls of the Concorde was its excessive working value, due partially to the large quantities of gas it required to succeed in high speeds. Specialists say in the present day’s supersonic jets will face comparable challenges.
Flying near the pace of sound adjustments the aerodynamics required of an plane, says Raymond Speth, affiliate director of the MIT Laboratory for Aviation and the Atmosphere. “All of the issues you must do to fly at supersonic pace,” he says, “they scale back your effectivity … There’s a cause we have now this candy spot the place airplanes fly in the present day, round Mach 0.8 or so.”
Growth estimates that considered one of its full-sized Overture jets will burn two to 3 instances as a lot gas per passenger as a subsonic aircraft’s first-class cabin. The corporate selected this comparability as a result of its plane is “designed to ship an enhanced, productive cabin expertise,” just like what’s out there in first- and business-class cabins on in the present day’s plane.
That baseline, nonetheless, isn’t consultant of the typical traveler in the present day. In comparison with customary economy-class journey, first-class cabins are likely to have bigger seats with more room between them. As a result of there are fewer seats, extra gas is required per passenger, and subsequently extra emissions are produced for every individual.